Income Distribution In Malaysia
We combine information obtained from national accounts household surveys fiscal data and demographic statistics.
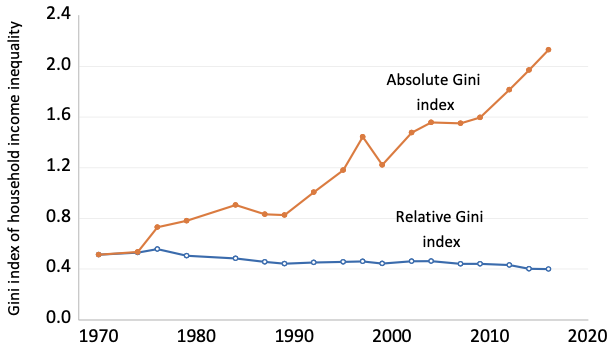
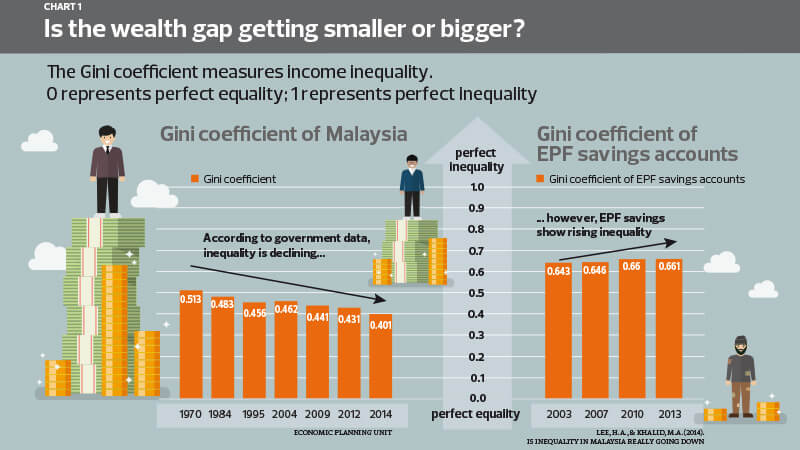
Income distribution in malaysia. Inequality measures are then applied to ascertain the levels of inequality based on this distribution. As the graph below shows over the past 31 years this indicator reached a maximum value of 10 10 in 2015 and a minimum value of 8 10 in 1997. Malaysia income distribution income share held by second 20.
In 2019 mean income in malaysia was rm7 901 while malaysia s median income recorded at rm5 873. Top 10 per cent malaysia. There was a large disparity in household incomes in malaysia as of 2016 with urban households earning on average 3 3 thousand ringgit more than rural households.
Equal split adults series income of married couples divided by two. The value for income share held by second 20 in malaysia was 10 10 as of 2015. In 2019 the average monthly income in malaysia is rm7 901.
Imputed rent is included in pre tax fiscal income and pre tax national income series. Malaysian household income survey data provided by the malaysian department of statistics is used to provide evidence that the upper tails of the household income distribution follows a fractal based distribution known as power law. There is a strong relationship between health status and education level on the income distribution and poverty in malaysia.
Income distribution for urban strata declined to 0 389 from 0 391 2014 whilst household income distribution for rural strata rose to 0 364 from 0 355 2014. The median household income will be rm15 000. Friday 10 july 2020 1200 household income basic amenities survey report 2019.
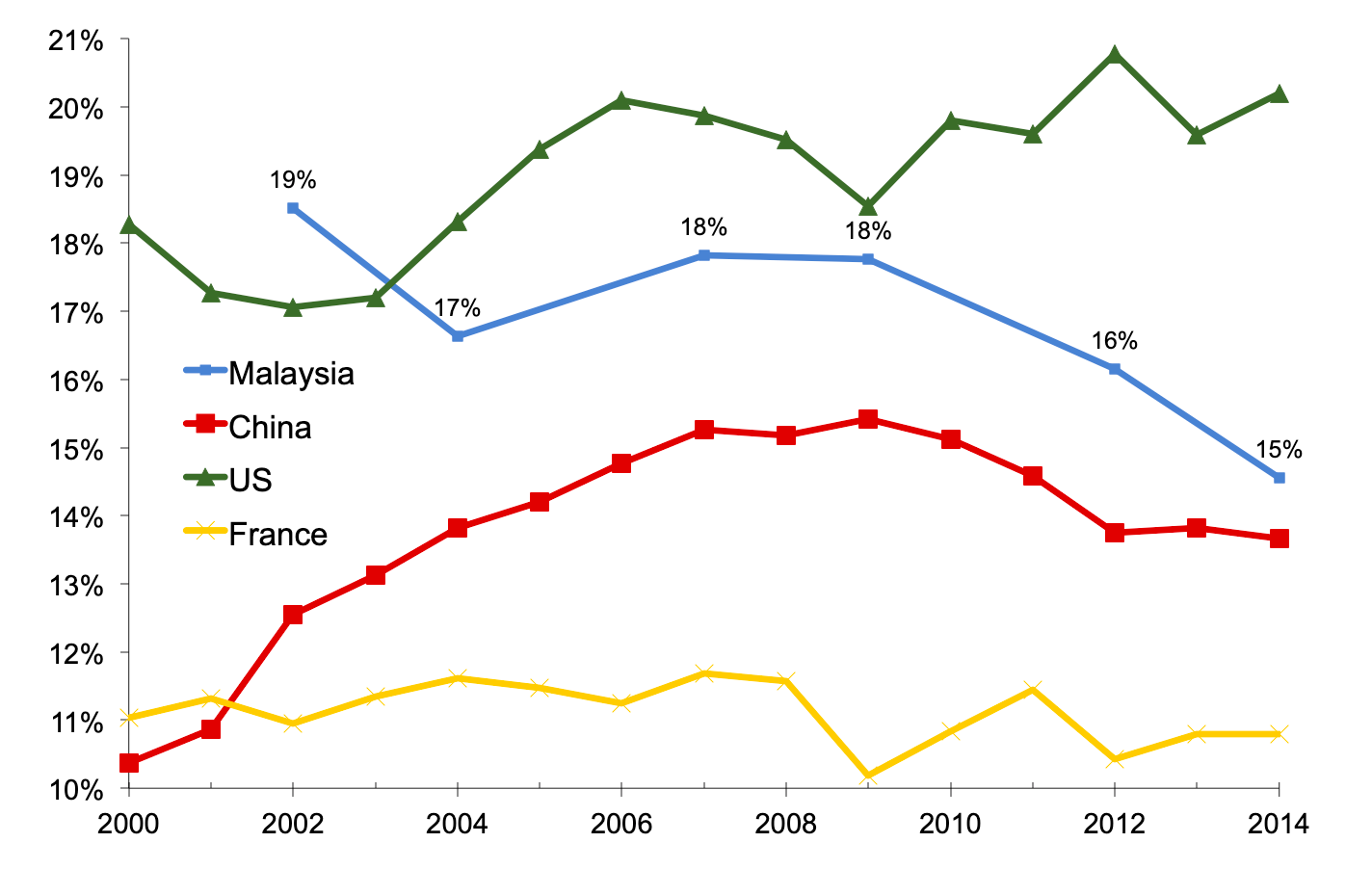
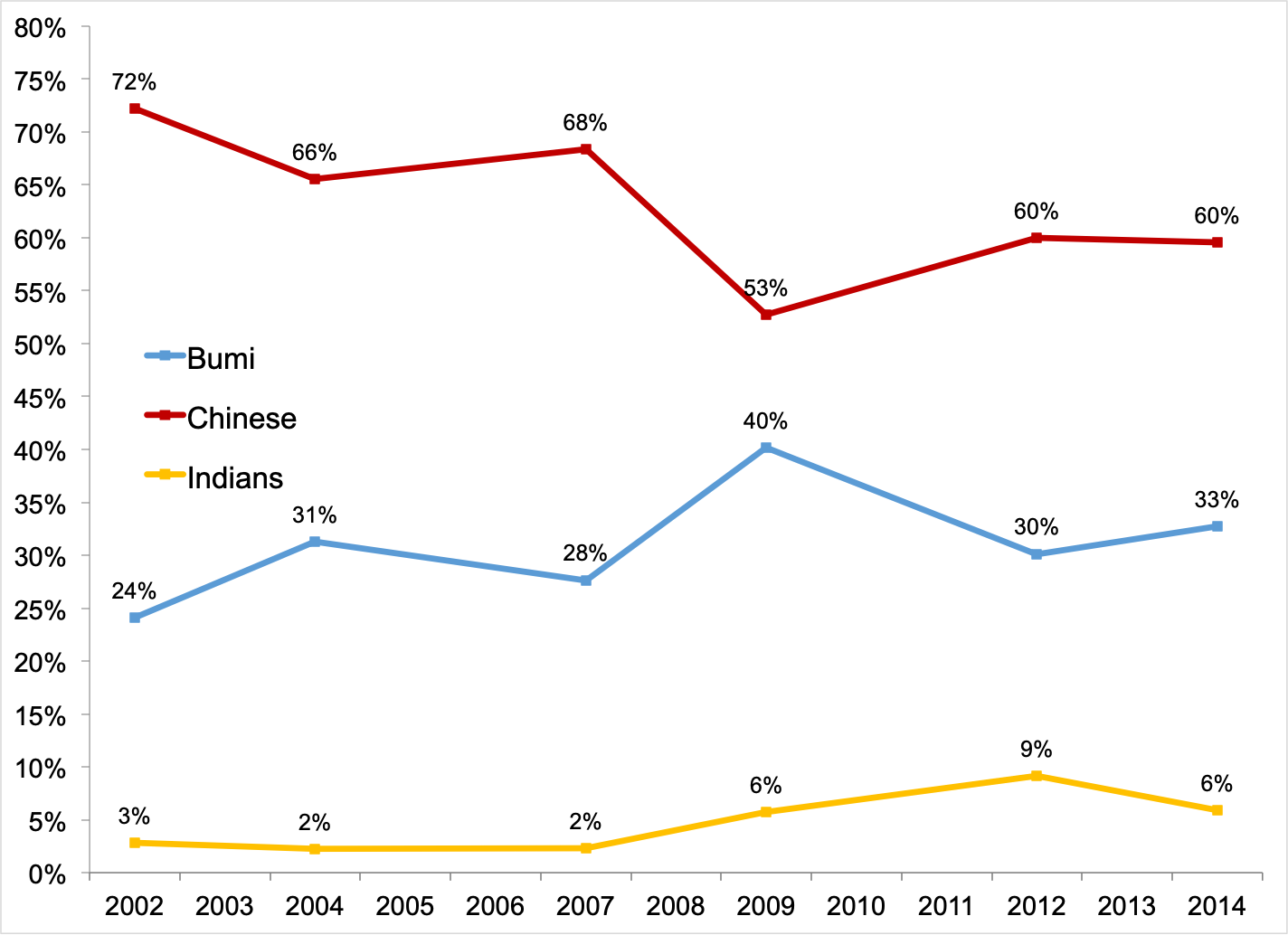
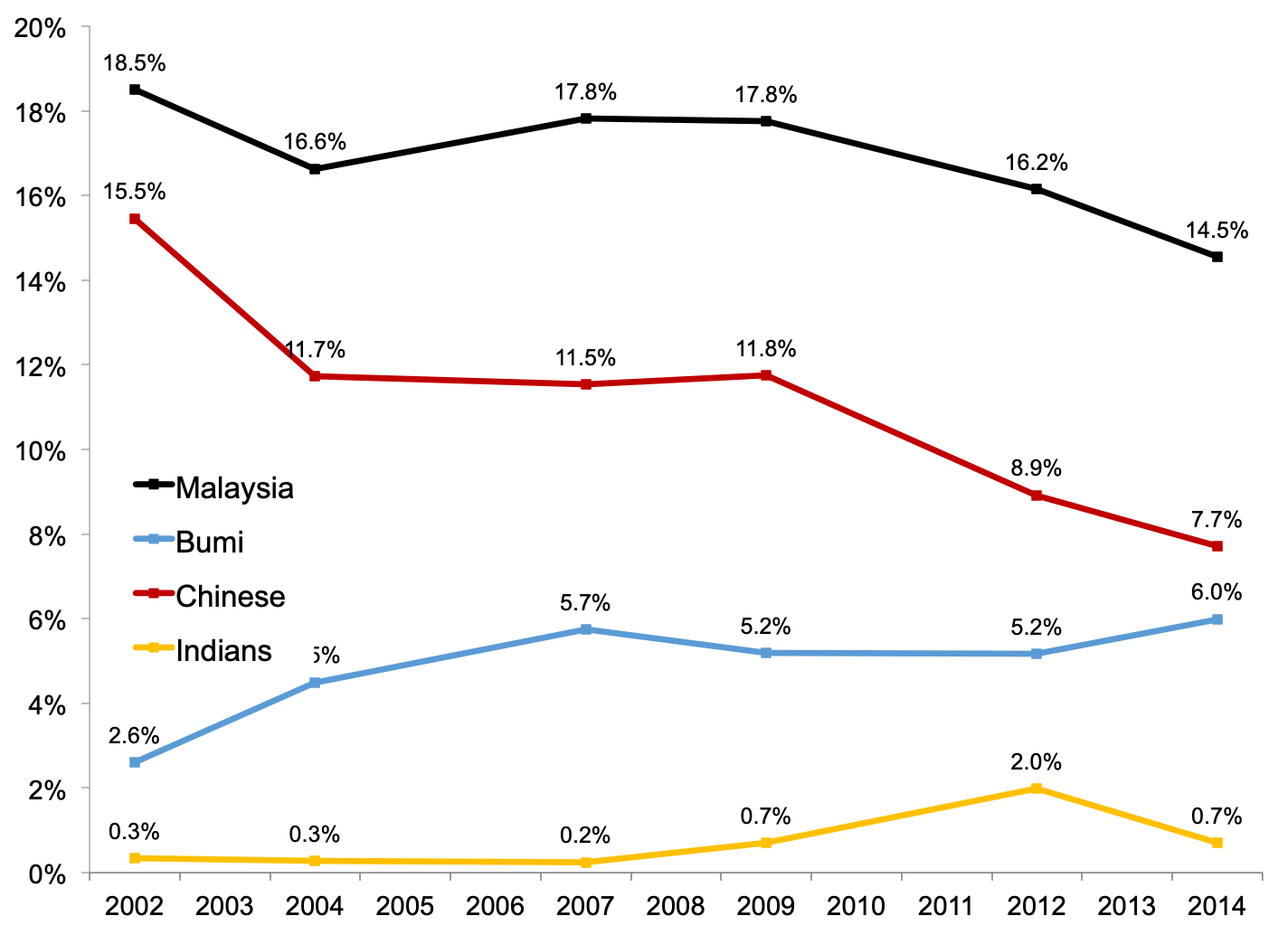
In this paper we document the evolution of income inequality in malaysia not only at the national level for the period of 1984 2014 but also by ethnic group for the period of 2002 2014. The mean monthly household consumption expenditure for malaysia increased from rm4 033 in 2016 to rm4 534 in 2019 which grew at 3 9 per cent per annum. Distribution of pretax national income before all taxes and transfers except pensions and unemployment insurance among adults.
The gini coefficient declined to 0 399 from 0 401 2014. Increase government wealth distribution efforts the increase of government spending in social expenditure has been proven to reduce the income inequality and lessen the poverty. In terms of growth median income in malaysia grew by 3 9 per cent per year in 2019 as compared to 6 6 per cent in 2016.
Income inequality and poverty is not satisfactory in malaysia. Specifically in the last decade the government has increased wealth distribution efforts which had a positive effect on the income equality in malaysia. This was largely due to the fact.
To our knowledge this is the first attempt to produce inequality measurements of. Moreover mean income rose. There is a gap of the income distribution between the educated and healthy people with the low income and unhealthy people in malaysia.
For example from 2009 to 2014 the real average household incomes of the bottom 40 grew at 11 9 per year compared to 7 9 of the total population of malaysia. The median is used because it represents a more accurate representation of the area than a mean number the average.